| Home | All Classes | Main Classes | Annotated | Grouped Classes | Functions |
The QRegion class specifies a clip region for a painter. More...
#include <qregion.h>
QRegion is used with QPainter::setClipRegion() to limit the paint area to what needs to be painted. There is also a QWidget::repaint() that takes a QRegion parameter. QRegion is the best tool for reducing flicker.
A region can be created from a rectangle, an ellipse, a polygon or a bitmap. Complex regions may be created by combining simple regions using unite(), intersect(), subtract() or eor() (exclusive or). You can move a region using translate().
You can test whether a region isNull(), isEmpty() or if it contains() a QPoint or QRect. The bounding rectangle is given by boundingRect().
The function rects() gives a decomposition of the region into rectangles.
Example of using complex regions:
void MyWidget::paintEvent( QPaintEvent * )
{
QPainter p; // our painter
QRegion r1( QRect(100,100,200,80), // r1 = elliptic region
QRegion::Ellipse );
QRegion r2( QRect(100,120,90,30) ); // r2 = rectangular region
QRegion r3 = r1.intersect( r2 ); // r3 = intersection
p.begin( this ); // start painting widget
p.setClipRegion( r3 ); // set clip region
... // paint clipped graphics
p.end(); // painting done
}
QRegion is an implicitly shared class.
Warning: Due to window system limitations, the whole coordinate space for a region is limited to the points between -32767 and 32767 on Mac OS X and Windows 95/98/ME.
See also QPainter::setClipRegion(), QPainter::setClipRect(), Graphics Classes, and Image Processing Classes.
Specifies the shape of the region to be created.
See also isNull().
If t is Rectangle, the region is the filled rectangle (x, y, w, h). If t is Ellipse, the region is the filled ellipse with center at (x + w / 2, y + h / 2) and size (w ,h ).
Create a region based on the rectange r with region type t.
If the rectangle is invalid a null region will be created.
See also QRegion::RegionType.
If winding is TRUE, the polygon region is filled using the winding algorithm, otherwise the default even-odd fill algorithm is used.
This constructor may create complex regions that will slow down painting when used.
The resulting region consists of the pixels in bitmap bm that are color1, as if each pixel was a 1 by 1 rectangle.
This constructor may create complex regions that will slow down painting when used. Note that drawing masked pixmaps can be done much faster using QPixmap::setMask().
Returns TRUE if the region overlaps the rectangle r; otherwise returns FALSE.
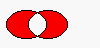
The figure shows the exclusive or of two elliptical regions.
Returns the region's handle.
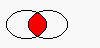
The figure shows the intersection of two elliptical regions.
Example:
QRegion r1( 10, 10, 20, 20 );
QRegion r2( 40, 40, 20, 20 );
QRegion r3;
r1.isNull(); // FALSE
r1.isEmpty(); // FALSE
r3.isNull(); // TRUE
r3.isEmpty(); // TRUE
r3 = r1.intersect( r2 ); // r3 = intersection of r1 and r2
r3.isNull(); // FALSE
r3.isEmpty(); // TRUE
r3 = r1.unite( r2 ); // r3 = union of r1 and r2
r3.isNull(); // FALSE
r3.isEmpty(); // FALSE
See also isNull().
A null region is a region that has not been initialized. A null region is always empty.
See also isEmpty().
Returns TRUE if the region is different from r; otherwise returns FALSE.
See also intersect().
See also intersect().
See also unite() and operator|().
See also intersect().
See also subtract().
See also subtract().
See also eor().
See also eor().
See also unite() and operator+().
See also unite().
The union of all the rectangles is equal to the original region.
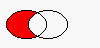
The figure shows the result when the ellipse on the right is subtracted from the ellipse on the left. (left-right )
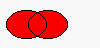
The figure shows the union of two elliptical regions.
Writes the region r to the stream s and returns a reference to the stream.
See also Format of the QDataStream operators.
Reads a region from the stream s into r and returns a reference to the stream.
See also Format of the QDataStream operators.
This file is part of the Qt toolkit. Copyright © 1995-2005 Trolltech. All Rights Reserved.
| Copyright © 2005 Trolltech | Trademarks | Qt 3.3.7
|